常用STL库的使用方法 记录了常用的STL使用方法
vector:数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <vector> vector<int> a(10);//初始化10个默认为0的数 vector<int> a(10,1);//初始化10个默认为1的数 vector<int> a; //初始化二维数组 vector<vector<int> > 2dVec(m ,vector<int>(n)); //m*n的二维vector,注意两个 "> "之间要有空格 2dVec.push_back({1, 2, 3});//可以这样加vector vector<vector<int> > 2dVec(m ,vector<int>(n,0)); //m*n的二维vector,所有元素初始化为0 a.push_back() a[0] a.front() //首元素 a.back() //尾元素 a.size() a.pop_back()//删除不输出 it = a.begin()+1 a.erase(it) it2 = a.begin()+3 a.erase(it,it2)//删除[it1,it2) a.clear() a.empty() a.insert(it,-1) vector<int>::iterator itDele; it = find(a.begin(), a.end(), 3);//查找3 if(it!=a.end())//如果找到了 //pair make_pair vector<pair<int ,int> > vp; vp.push_back({1, 0}); vp.push_back(make_pair(0, 1)); vector<pair<int, int> > vp2 = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}}; vp2.push_back(make_pair<int, int>(5, 6));
list:数组 Lists将元素按顺序储存在链表中. 与向量(vectors)相比, 它允许快速的插入和删除,但是随机访问却比较慢。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include <list> pop_back() 删除最后一个元素 pop_front() 删除第一个元素 push_back() 在list的末尾添加一个元素 push_front() 在list的头部添加一个元素 back() 返回最后一个元素 front() 返回第一个元素 begin() 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 end() 返回末尾的迭代器 size() 返回list中的元素个数 clear() 删除所有元素 empty() 如果list是空的则返回true a.sort() 给list排序 erase() 删除一个元素 assign() 给list赋值 get_allocator() 返回list的配置器 insert() 插入一个元素到list中 max_size() 返回list能容纳的最大元素数量 merge() 合并两个list rbegin() 返回指向第一个元素的逆向迭代器 remove() 从list删除元素 remove_if() 按指定条件删除元素 rend() 指向list末尾的逆向迭代器 resize() 改变list的大小 reverse() 把list的元素倒转 splice() 合并两个list swap() 交换两个list unique() 删除list中重复的元素
stack:栈 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 #include <stack> stack<int> a; a.push() a.top() a.pop() a.empty() a.size()
queue:队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 #include <queue> queue<int> a; a.push() a.front() a.back() a.pop() a.empty() a.size()
priority_queue:堆 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <queue> //priority_queue<type,container,function> //小根堆,a>b priority_queue <int,vector<int>,greater<int> > q; //大根堆,a<b priority_queue <int,vector<int>,less<int> > q; //默认是大根堆 priority_queue <int> q ; //自定义堆的比较方式 //方法1,用类 class cmp { public: bool operator()(const pair<int, int> &a, const pair<int, int> &b){ return a.second > b.second; //a>b = greater<int> } }; //方法2,用struct struct cmp { bool operator()(const pair<int, int> &a, const pair<int, int> &b){ return a.second > b.second; } }; priority_queue<pair<int, int>,vector<pair<int,int> >, cmp> pq; //注意!没有front和back q.push() q.pop() q.top() q.empty() q.size()
map/unordered_map 哈希表的实现:STL中,map/set 对应的数据结构是红黑树。红黑树是一种近似于平衡的二叉查找树,里面的数据是有序的。在红黑树上做查找操作的时间复杂度为 O(logN)。而 unordered_map/unordered_set 对应 哈希表,哈希表的特点就是查找效率高,时间复杂度为常数级别 O(1), 而额外空间复杂度则要高出许多而且无序。所以对于需要高效率查询的情况,使用 unordered_map 容器。而如果对内存大小比较敏感或者数据存储要求有序的话,则可以用 map 容器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <map> std:map<int,int> mapA; //插入 mapA.insert(std::pair<int,int>(0,1)); mapA.insert(map<int,int>::value_type (0,1)); mapA[0] = 1; mapA.at(0) mapA.size() map<int, int>::iterator iter;//迭代器 mapA.erase(key/iter) mapA.clear() mapA.empty() mapA.count() //由于map不包含重复的key,因此m.count(key)取值为0,或者1,表示是否包含。 mapA.find(key)//返回迭代器,判断是否存在。 mapA.find(key) != mapA.end() //为真说明存在 #include <unordered_map> //和map差不多
map的注意事项:
在map中,由key查找value时,首先要判断map中是否包含key。
如果不检查,直接返回map[key],可能会出现意想不到的行为。如果map包含key,没有问题,如果map不包含key,使用下标有一个危险的副作用,会在map中插入一个key的元素,value取默认值,返回value。也就是说,map[key]不可能返回null。
比如:
1 2 3 4 unordered_map<string, int> mapA; cout << mapA.size() << endl; //这时为0 int a = mapA["aa"] //本来是空map,但是调用mapA["aa"]之后,会自动插入mapA["aa"]=0,返回0 cout << mapA.size() << endl; //这使为1
set/multiset/unordered_set set和multiset的区别:
set不可以有重复的元素
multiset可以有重复的元素
和map/unordered_map一样,也是set/multiset使用红黑树实现,unordered_set使用哈希表实现。unordered_set和unordered_map内部实现的公共接口大致相同。
set是按照一定的次序存储元素的容器,set遍历后有序,默认按照小于排序
set中只放value,但是底层存放的是<value, value>的键值对。每个value必须是惟一的
set允许插入和删除,不允许修改
set按照内部比较对象(类型比较)所指示的特定严格弱排序准则进行排序
set在底层用二叉搜索树(红黑树)实现
set中查找、插入、删除元素的复杂度为O(logn),unordered_set为O(1)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <set> #include <unordered_set> unordered_set<int> us; us.insert(2);//插入 unordered_set<int> us1(us);//us1=us unordered_set<int> us2(us1.begin(),us1.end()); us.erase(6); //删除键值为6的元素 set<int>::iterator it; it = us.find(6); //查找键值为6的元素 int n = us.count(6);//也能判断一个数是否在集合中。n=0不在,n=在 set<int> s = {3,8,12,15} s.lower_bound(8); //表示查找 >= 8 的元素中最小的一个(8),并返回指向该元素的迭代器 s.upper_bound(8); //表示查找 >8 的元素中最小的一个(12),并返回指向该元素的迭代器 s.lower_bound(9); //12 s.upper_bound(9); //12 begin() //返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 clear() //清除所有元素 count() //返回某个值元素的个数 empty() //如果集合为空,返回true end() //返回指向最后一个元素的迭代器 equal_range() //返回集合中与给定值相等的上下限的两个迭代器 erase() //删除集合中的元素 find() //返回一个指向被查找到元素的迭代器 get_allocator() //返回集合的分配器 insert() //在集合中插入元素 lower_bound() //返回指向大于(或等于)某值的第一个元素的迭代器 key_comp() //返回一个用于元素间值比较的函数 max_size() //返回集合能容纳的元素的最大限值 rbegin() //返回指向集合中最后一个元素的反向迭代器 rend() //返回指向集合中第一个元素的反向迭代器 size() //集合中元素的数目 swap() //交换两个集合变量 upper_bound() //返回大于某个值元素的迭代器 value_comp() //返回一个用于比较元素间的值的函数
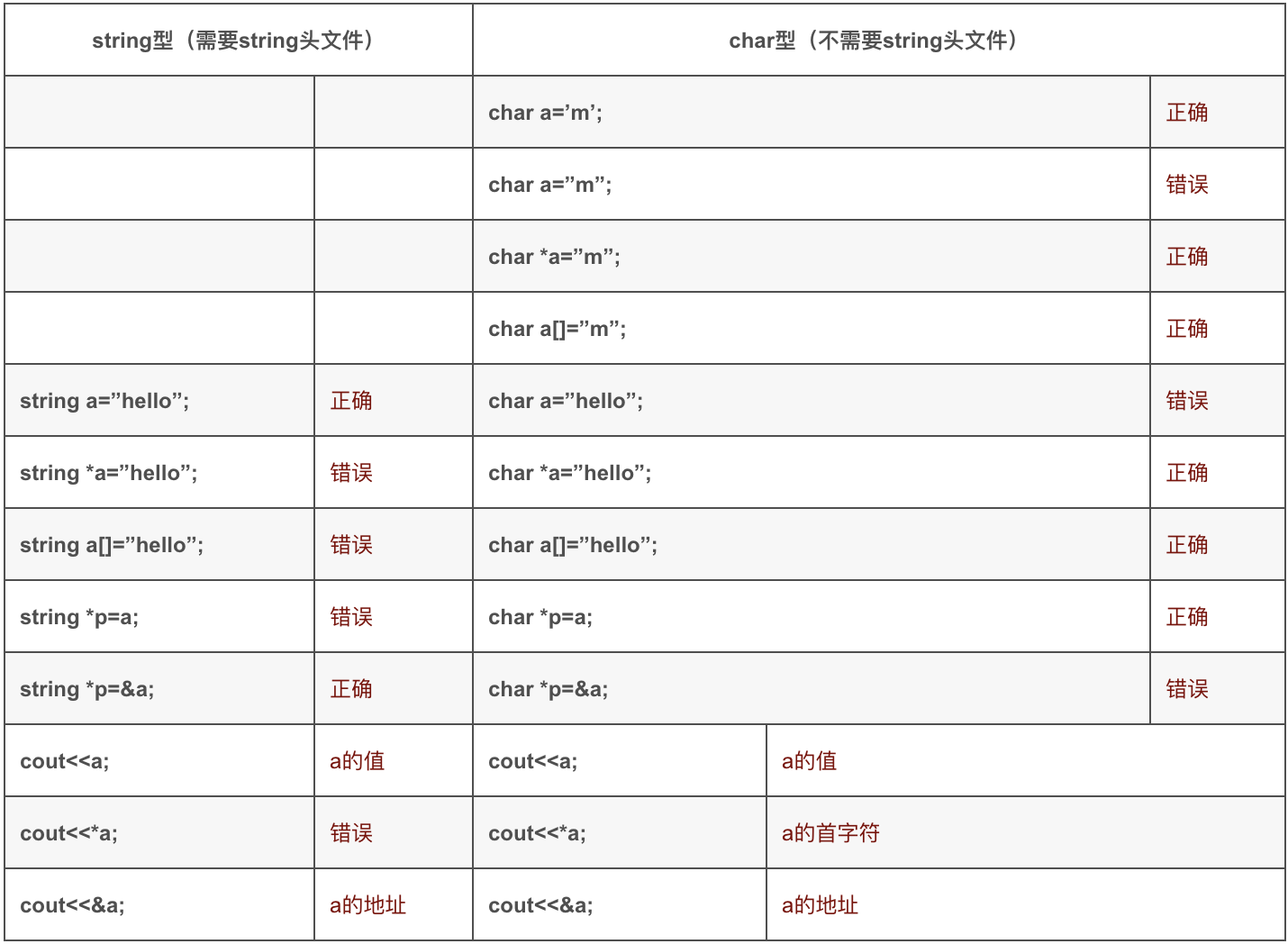
string 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <string> string s; s.find()//在s当中查找第一个出现 s.rfind()//在s当中查找最后一个出现 int is = stoi(val) //把string val转换成int。stoi()会做范围检查,默认范围是在int的范围内的,如果超出范围的话则会runtime error int is = atoi(val.c_str()) //atoi()不会做范围检查,如果超出范围的话,超出上界,则输出上界,超出下界,则输出下界 #include <algorithm> reverse(s.begin(),s.end()); //反转字符串 #include <cstring> //s1 s2需要c风格字符串char //如果是string,需要s1.c_str() strcmp(s1,s2) //相等返回0;s1-s2大于0,则返回1,小于0则返回-1 strncmp(s1,s2,n) //比较前n个 strcpy(s1,s2) //s2复制到s1,注意s2不要比s1长
大小写转换
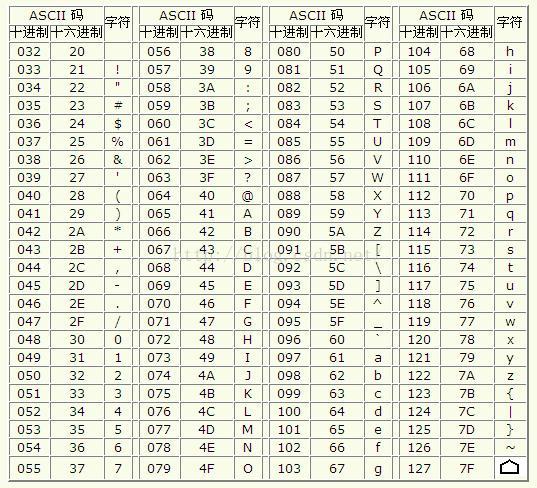
对应大小写字母之间相差32 transform函数:直接处理string1 2 3 string s = "aBc"; transform(s.begin(), s.end(), s.begin(), ::tolower);//::toupper转大写
toupper, tolower:处理char1 2 3 4 5 #include <cctype> char s = 'a'; char sl = tolower(s); char su = toupper(sl);
algorithm sort sort并非只是普通的快速排序 ,除了对普通的快速排序进行优化,它还结合了插入排序 和堆排序 。根据不同的数量级别以及不同情况,能自动选用合适的排序方法。当数据量较大时采用快速排序,分段递归。一旦分段后的数据量小于某个阀值,为避免递归调用带来过大的额外负荷,便会改用插入排序。而如果递归层次过深,有出现最坏情况的倾向,还会改用堆排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <algorithm> //nums必须是线性容器 //降序排序 sort(nums.begin(),nums.end(),greater<int>()); //升序(默认是升序) sort(nums.begin(),nums.end(),less<int>()); sort(nums.begin(),nums.end()); //自定义排序函数 vector<vecotr<int> > nums2d; bool cmp(const vector<int> &a, const vector<int> &b){ //注意!这个函数要在类外面定义 return a[1] > b[1];//按第二维降序 } sort(nums2d.begin(),nums2d.end(),cmp); //稳定排序 stable_sort(nums.begin(),nums.end(),greater<int>()); stable_sort(nums.begin(),nums.end(),less<int>());
sort算法有个限制,利用sort算法只能对序列容器 进行排序,就是线性的,如vector,list,deque 。map也是一个集合容器,但它里面存储的元素是pair,不是线性存储的(前面提过,像红黑树),所以利用sort不能直接和map结合进行排序。
如果想对map进行排序,可以把map放到vector中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 // 将map中的内容转存到vector中 vector<pair<string, int> > vec(map.begin(), map.end()); bool cmp(const pair<string, int>& a, const pair<string, int>& b) { return a.second < b.second; } //对线性的vector进行排序 sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp);
注意:
支持随机存取迭代器(连续存储空间)的vector,deque (双向存取的vector)可以使用sort;
支持随机存取迭代器(链式非连续存储空间)的list(双向链表)和slist(单向链表forward_list),不能使用STL的sort,但是类中有自定义的sort()成员函数;
关系型容器中基于红黑树的set,multiset,map,multimap,本身就有自动排序的功能,不需要sort函数。如果有特殊排序需求的话,可以放入vector中;
stack,queue没有迭代器,入口出口固定,不能进行排序;基于哈希表的unordered_map等都是为排序的,也不需要排序。
count 1 2 3 4 #include <algorithm> vector<int> nums = {100,100,100,101}; int num = count(nums.begin(),nums.end(),100);//统计100出现的次数
lower_bound、upper_bound、binary_search 1 2 3 4 5 #include <algorithm> lower_bound(起始地址,结束地址,要查找的数值) //返回的是数值 第一个 出现的位置。 upper_bound(起始地址,结束地址,要查找的数值) //返回的是数值 最后一个 出现的位置。 binary_search(起始地址,结束地址,要查找的数值) //返回的是是否存在这么一个数,是一个bool值。
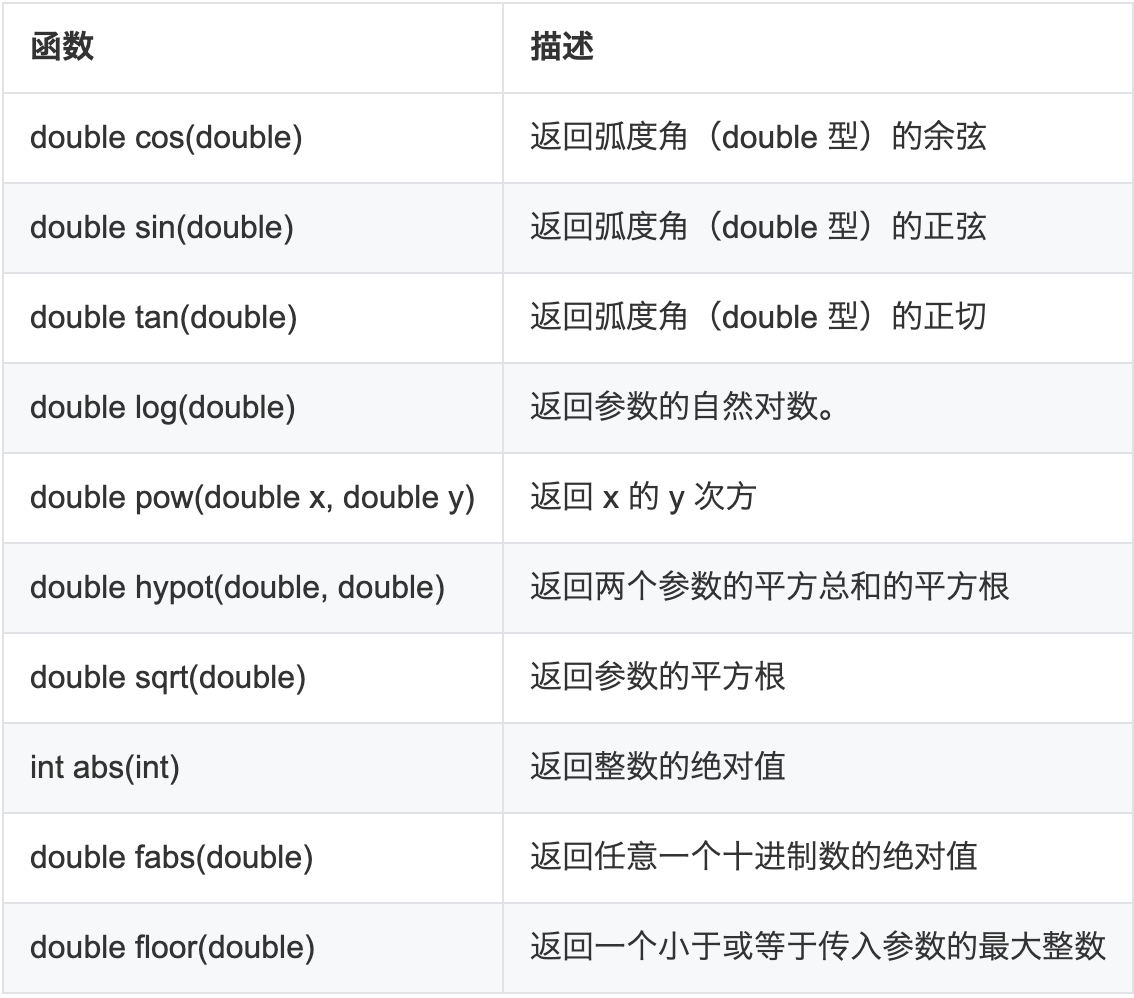
一些数学运算
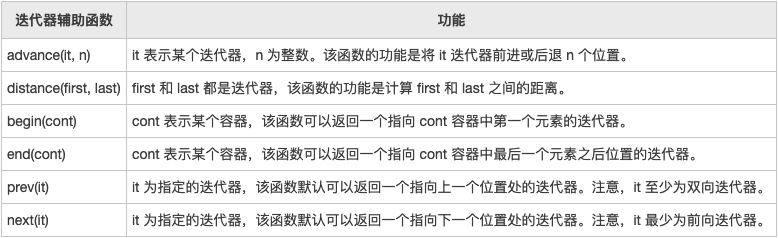
迭代器
cctype 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include <cctype> isalnum(c)//当c是字母或数字时为真 isalpha(c)//当c是字母时为真 isdigit(c)//当c是数字时为真 islower(c)//当c是小写字母时为真 isupper(c)//当c是大写字母时为真 isspace(c)//当c是空白时为真(即c是空格、横向制表符、纵向制表符、回车符、换行符、进纸符) iscntrl(c)//当c是控制字符时为真 isgraph(c)//当c不是空格但可打印时为真 isprint(c)//当c是可打印字符时为真(即c是空格或c具有可视形式) ispunct(c)//当c是标点符号时为真 isxdigit(c)//当c是十六进制数字时为真 tolower(c)//如果c是大写字母,输出对应的小写字母,否则原样输出c toupper(c)//如果c是小写字母,输出对应的大写字母,否则原样输出c